Addition: GLUT is a powerful but simple windows manager. We can not make some OS-like operations like hiding window's header or keep window always on top of other windows.
Problem: use separate GLUT windows with own callbacks and drawing functions.
Example: written on C++, freeglut.
Languages:
EN,
RU
Created window inherits OS's windows style.
At pictures it is running on Ubuntu 16.04LTS.

Addition: GLUT is a powerful but simple windows manager. We can not make some
OS-like operations like hiding window's header or keep window always on top of
other windows.
We initializing two windows sequently. For each write own display function.
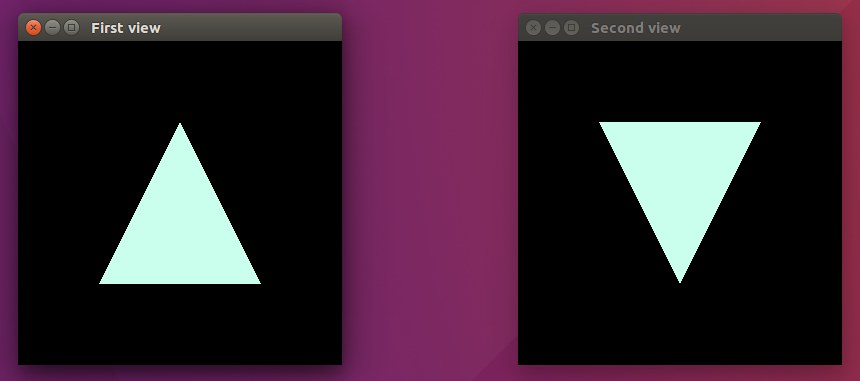
Generally, problem is solved. But in future we may want to have more than two
windows and with more harder callbacks logic. Let's try encapsulate window
managment inside class for more scalability.
Make step backward to single window problem and implement class with same usage.
Header of our class has all that we need. User choose window title only. Now main function use single line for create similar window. In sight of class user it is easy to use without care about internal implementation.
In sight of class we just encpsulated existing usage inside corresponding methods. Note that functions is static. It is required for registering callbacks.
We need to provide few windows management. Due to display function is static, it
is same for different class objects. But we need to separate displaying.
Let's make display as abstract function that will be implemented inside
an inherited classes. As callback we calling each display of created window.
We will see that display_all function is registered as callback for each window i.e. in case of single display request we redisplay every other window.
For new window we implements class with own display.
In addition let's try merge two windows inside single window. But each subwindow
has own callbacks.
GLUT has method glutCreateSubWindow(..) which creates new window in space of
existing parent window.
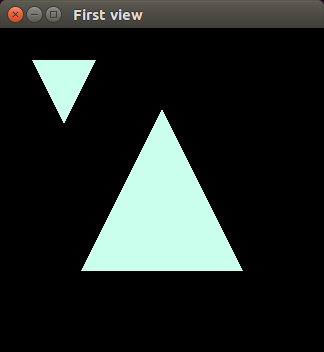
Addition: subwindow has constant shape although parent size changes. If needed, we can make own child reshape using relative coordinates and parent's reshape callback.